Arrays#
Key Ideas#
Storing sets of data
Arrays
Readings#
https://books.trinket.io/thinkjava2/chapter7.html
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/arrays.html
Definition
Array - An array is a data structure that contains a group of elements of a fixed size. They are used to store sets of data like golf scores, budgets, etc. where data is stored like a “grid”.
Concepts#
Visualization#
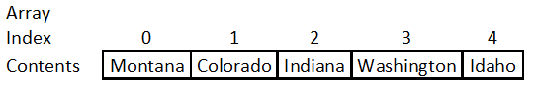
Index - the index identifies the location of the data.
Element - the box itself is referred to as an element
// This is a one dimensional array
String[] states = new String[5];
// set values - include the index and value
states[0] = "Montana";
states[1] = "Colorado";
states[2] = "Indiana";
states[3] = "Washington";
states[4] = "Idaho";
//alternative method
String[] states2 = {"Montana","Colorado","Indiana","Washington","Idaho"};
// retrieve value
String astate;
astate = states[2];
System.out.print(astate);
// output is Indiana
Tip
In the majority of programming languages, the first index starts at 0.
2 Dimensional Array#
Assume the following array. It is tracking states, their capitals, state bird, and state rock. It is named stateData.
The “[ ]” are there for reference only. The squares “[ ]” indicate the coordinate system. They are not part of the actual data - they are there for reference only. Note that the coordinates are [row, column].
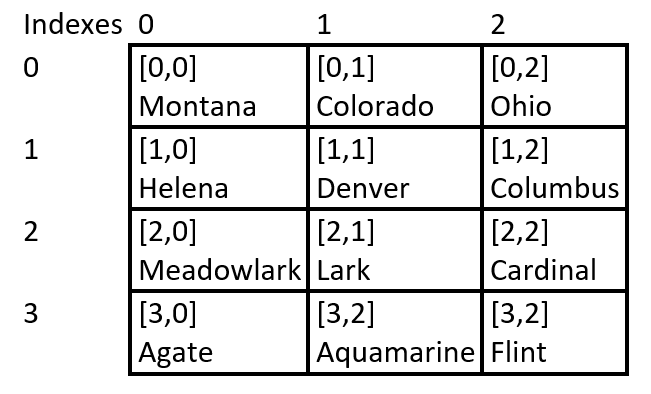
// create the 2 dimensional array
String[][] stateData =
{
{"Montana", "Colorado", "Ohio"},
{"Helena", "Denver", "Columbus"},
{"Meadolark", "Lark", "Cardinal"},
{"Agate", "Aquamarine", "Flint"}
};
// output some data
String myData = "";
myData = stateData[1][1];
System.out.println("Capital of Colorado is " + myData);
myData = stateData[2][0];
System.out.println("The state bird of Montana is " + myData);
myData = stateData[0][2];
System.out.println("The state is " + myData);
// change Montana's state bird to hawk
myData = "Hawk";
stateData[2][0] = myData;
myData = stateData[2][0];
System.out.println("The state bird of Montana is " + myData);
// to iterate through the 2 dimensional array
int Rows = 4;
int Cols = 3;
// this for statement controls the rows
// note that r will keep track of the index of the rows
for(int r = 0; r < Rows; r++)
{
// this for statement controls the columns
// note that c will keep track of the index of the columns
for(int c = 0; c < Cols; c++)
{
System.out.print(stateData[r][c] + " ");
}
// code is now at the end of a "row"
// move the cursor down
System.out.println();
}
/*
Output
Capital of Colorado is Denver
The state bird of Montana is Meadolark
The state is Ohio
The state bird of Montana is Hawk
*/
Lecture Code#
/*
Programmer: James Goudy
Project: Array Lecture Code
ANT project
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array_Lecture {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Variables
//declare an arrays
double[] Array1;
String[] DogName;
int[] Scores;
double[][] Grid3by2;
//Variables
String ADogName;
String stryy;
//Variables for printing grid
int Colcntr = 0;
int ColStop = 2;
int Rowcntr = 0;
int RowStop = 3;
//Initalize the array
//This is where we set how many elements we need.
//Consider an element as a box to store the data
Array1 = new double[5]; //We can store 5 doubles
DogName = new String[3]; //Here we can store 3 names
Scores = new int[4]; //Here we can store 4 scores
Grid3by2 = new double[3][2];
//Here is an example of how we can
//create and initialize an array in one step
String[] colors = {"Red", "Green", "Blue"};
String[][] names = {{"Mr. ", "Mrs. ", "Ms. "}, {"Smith", "Jones", "Rodes"}};
//How we enter values into an array
DogName[0] = "Fido";
DogName[1] = "Spot";
DogName[2] = "Barky";
//Assign an element to a variable:
ADogName = DogName[1]; // This assigns the value of Spot to ADogName
System.out.println("The second dog is " + ADogName);
//Print the name out by referencing the array element
System.out.println("The second dog is " + DogName[1]);
//Here is how we enter data into Grid3by2
//Here is the data in the grid formataion
// 10 | 15
// -- | --
// 20 | 25
// -- | --
// 30 | 35
Grid3by2[0][0] = 10;
Grid3by2[0][1] = 15;
Grid3by2[1][0] = 20;
Grid3by2[1][1] = 25;
Grid3by2[2][0] = 30;
Grid3by2[2][1] = 35;
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
//Loop to control rows
while (Rowcntr < RowStop) {
//Loop to control columns
while (Colcntr < ColStop) {
System.out.print(Grid3by2[Rowcntr][Colcntr] + " ");
Colcntr++;
}
Colcntr = 0;
System.out.println();
Rowcntr++;
}
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
//using a for to loop through an array
for (String d : DogName) {
System.out.println(d);
}
//An example of using a for statement to print
// an array - note that in this example we are storing
//the array value in myValue and then printing it.
//
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
double myValue;
// Note how the counters row and col will always increment
// to the coordinates of current element
for (int row = 0; row < 3; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < 2; col++) {
myValue = Grid3by2[row][col];
System.out.print(myValue + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
//Short hand version of using a for statement
for (double[] dx : Grid3by2) {
for (double dy : dx) {
System.out.print(dy);
}
System.out.println();
}
///////////////////////////////////////
//Sort an Array
///////////////////////////////////////
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
int[] Numbers1 = {5, 2, 4, 3, 0, 7, 1, 6};
for (int NumCntr = 0; NumCntr < Numbers1.length; NumCntr++) {
System.out.print(Numbers1[NumCntr] + " ");
}
Arrays.sort(Numbers1);
System.out.print("\n\n");
for (int NumCntr = 0; NumCntr < Numbers1.length; NumCntr++) {
System.out.print(Numbers1[NumCntr] + " ");
}
///////////////////////////////////////
//Search an Array
///////////////////////////////////////
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
String SearchItem;
int FoundItem;
String[] vehicles = {"bicycle", "truck", "car", "atv",
"segway", "motor home", "skate board",
"airplane", "boat", "canoe"};
SearchItem = "segway";
Arrays.sort(vehicles);
//Binary Search searches for the item
//If found, it will return the index
//If not found, it will return a -1
//Note Arrays must be sorted first in order to
//return accurate results
FoundItem = Arrays.binarySearch(vehicles, SearchItem);
if (FoundItem > -1) {
System.out.println("Founditem is " + vehicles[FoundItem]);
} else {
System.out.println("Vehicle not found");
}
///////////////////////////////////////
//Fill an Array
///////////////////////////////////////
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
//Replaces all the values with the value 99
Arrays.fill(Numbers1, 99);
for (int NumCntr = 0; NumCntr < Numbers1.length; NumCntr++) {
System.out.print(Numbers1[NumCntr] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n\n");
//Fill the first three spots withthe number 42
Arrays.fill(Numbers1, 0, 3, 42);
for (int NumCntr = 0; NumCntr < Numbers1.length; NumCntr++) {
System.out.print(Numbers1[NumCntr] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n\n");
Arrays.fill(vehicles, "");
for (int NumCntr = 0; NumCntr < vehicles.length; NumCntr++) {
System.out.print(vehicles[NumCntr] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n----------------\n");
}
}
End Of Topic