Combo boxes#
Major Properties and Events#
JAVA combo boxes, also known as JComboBox in Swing is a versatile component that allow users to select a single item from a list. They offer a user-friendly way to present a set of options and improve data entry efficiency. Here are some of the major properties of a Java combo box:
Basic Properties:
Items: The core property of a combo box is its list of items. You can add, remove, and modify items programmatically or through a visual editor.
Selected Item: The combo box always has a selected item, which is the currently chosen option displayed in the text field.
Java combo box selected item
Editable: You can configure the combo box to be editable or non-editable. In editable mode, users can type their own values, while non-editable mode restricts them to selecting from the predefined list.
Enabled: This property determines whether the combo box is interactable or disabled (grayed out).
Advanced Properties:
Model: The combo box model manages the underlying data and presentation of the items. You can use different model implementations for more complex scenarios.
Renderer: The renderer controls how each item is displayed in the list. You can customize the appearance of the items using custom renderers.
Popup Visible: This property controls whether the dropdown list is currently visible. You can programmatically show or hide the list.
Maximum Row Count: This property limits the number of visible items in the dropdown list. If there are more items, a scrollbar appears.
Event Handling:
Item Selection: When the user selects an item, a selection event is fired. You can listen to these events to react to user choices.
Action Events: In editable mode, typing Enter or clicking outside the text field triggers an action event. You can use this event to capture user input.
These are just some of the major properties of Java combo boxes. By understanding and manipulating these properties, you can create flexible and user-friendly interfaces for your applications.
Lecture Code Summary#
Overall Structure
The entry point is the
mainmethod in theJ2x_20_comboBoxesclass.Inside
main, aComboBoxDemoobject is created. That object sets up the entire GUI in its constructor.
GUI Setup The GUI is built using Swing components (JFrame, JLabel, JTextField, JButton, JComboBox) and a manual (absolute) layout.
Manual Layout
: The code calls
jf1.setLayout(null)
, which disables the default layout managers. Each component’s size and position are set explicitly via
setSize()
and
setLocation()
.
Pros: Direct control over positioning.
Cons: Not easily resizable or adaptive, and can be cumbersome if the UI must scale or localize.
Helper Methods
The constructor for ComboBoxDemo calls various private methods, each dedicated to setting up a particular type of component. This is a clean approach for readability and code reuse:
setUpTheJFrame(JFrame, int, int, String, Color, boolean)Configures theJFramesize, title, background color, close operation, visibility, and layout.setupLabel(...)Creates and positions aJLabelwith the desired text and font size.setupTextFields(...)Creates aJTextField, positions it, and sets basic properties like font and visibility.setupCombo(...)Initializes theJComboBox. If aString[]is provided, all those items are added to it. It also attaches anActionListenerthat updateslblSelectedeach time a new item is chosen.setTheButtons(...)Creates aJButtonwith the given text, size, and location. It then attaches both anActionListener(listening for button clicks) and aKeyListener(listening for the Enter key), both of which call a shared handler method (theButtonAction).
Button Actions
The theButtonAction(String bttnText) method handles all the button clicks (and the Enter key on the button). The parameter bttnText is matched against the button label to determine which operation to perform. Specifically:
“Add Item” Reads text from
txtFieldand, if non-empty, appends it to the combo box (comboBox.addItem(...)).“Remove Selected” Removes the currently selected item (
comboBox.removeItemAt(comboBox.getSelectedIndex())).“Remove Last” Removes the last item in the combo box (
comboBox.removeItemAt(comboBox.getItemCount()-1)).
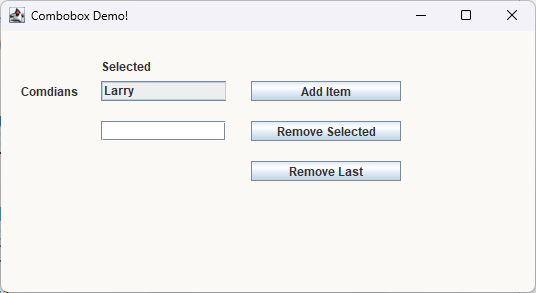
Lecture Code#
/*
Progam: Combo Box
Function: The purpose of the program is demostrate the
selection of a combobox, add items and subtract items,
of a combobox programmically
Programmer: James Goudy ©2024
*/
package j2x_20_comboboxes;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.KeyListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
/**
* Class ComboBoxDemo demonstrates a GUI with a ComboBox (drop-down list),
* including adding, removing selected, and removing the last item.
*/
class ComboBoxDemo {
// This array holds the initial set of comedian names for the combo box
String[] comedians = {"Larry", "Curly", "Moe", "Shemp", "Curly Joe"};
// Create a JFrame instance for the application window
JFrame Frame1 = new JFrame();
// Label to prompt or describe the comedian list
JLabel lblComedians = new JLabel();
// Label to display the currently selected item from the combo box
JLabel lblSelected = new JLabel();
// Text field for user to type a new item to add into the combo box
JTextField txtField = new JTextField();
// Button to remove the currently selected item from the combo box
JButton bttnRemoveSelected = new JButton();
// Button to add a new item from the text field to the combo box
JButton bttnAddItem = new JButton();
// Button to remove the last item in the combo box
JButton bttnRemoveLast = new JButton();
// JComboBox to display the set of comedians and any new items
// the user might add
//JComboBox comboBox = new JComboBox(comedians);
JComboBox comboBox = new JComboBox();
/**
* Constructor initializes and lays out all the GUI components.
*/
public ComboBoxDemo() {
float lblFontSize = 12f;
int xWidth = 125;
int aWidth = 150;
// Define a custom background color
Color myColor = new Color(250, 249, 246);
// Set up the JFrame with size, title, background, etc.
setUpTheJFrame(Frame1, 550, 300, "Combobox Demo!",
myColor , true);
// Set up labels, combo box, text field, and buttons
setupLabel(Frame1, lblSelected, 100, 25,150, "Selected", lblFontSize);
setupLabel(Frame1, lblComedians, 20, 50, 150, "Comdians", lblFontSize);
setupCombo(Frame1, comboBox, 100, 50, xWidth, lblFontSize, comedians);
setupTextFields(Frame1, txtField, 100, 90, xWidth, lblFontSize);
setTheButtons(Frame1, bttnAddItem, 250, 50, aWidth, "Add Item",
lblFontSize);
setTheButtons(Frame1, bttnRemoveSelected, 250, 90,
aWidth, "Remove Selected", lblFontSize);
setTheButtons(Frame1, bttnRemoveLast, 250, 130, aWidth, "Remove Last",
lblFontSize);
}
// Private method to configure the JFrame's visual
// and behavioral properties
private void setUpTheJFrame(JFrame jf1, int frameWidth, int frameHeight,
String frameTitle, Color frameColor,boolean turnLayoutManagerOff) {
// Set the initial dimensions of the JFrame's window
jf1.setSize(frameWidth, frameHeight);
// Set the JFrame title
jf1.setTitle(frameTitle);
// Apply a custom background color to the content pane
// The content pane is the area where items are added to
// the frame
jf1.getContentPane().setBackground(frameColor);
// Make the JFrame visible on the screen,
// allowing users to interact with it
jf1.setVisible(true);
// Center the JFrame on the user's screen for optimal visibility
jf1.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
// Specify the program's termination behavior
// when the JFrame is closed
// Exit the program when the frame is closed
jf1.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Disable the default layout manager, allowing
// for manual component positioning
// Note: Manual layout can be more complex to manage
// disable the default layout manager
if (turnLayoutManagerOff) {
jf1.setLayout(null);
}
}
/**
* Helper method to set up a JLabel with custom position,
* size, text, and font size.
*/
private void setupLabel(JFrame jf1, JLabel lbl,
int xpos, int ypos, int lblWidth,
String theText, float labelSize) {
// Set the font size to 12 points
// NOTE: Have to do this before we add the text
lbl.setFont(lbl.getFont().deriveFont(labelSize));
// Set the preferred size of the label
lbl.setSize(lblWidth, (int) labelSize + 8);
// Set the text content of the label
lbl.setText(theText);
// Make the label visible
lbl.setVisible(true);
// Position the label at coordinates (xpos, ypos) within the window
lbl.setLocation(xpos, ypos);
// Add the label to the window's content pane
jf1.add(lbl); // Assuming jf1 is the main window object
// Request the window to be redrawn, reflecting the added label
jf1.repaint();
}
/**
* Helper method to set up a JTextField with the specified
* position, width, and font size.
*/
private void setupTextFields(JFrame jf1, JTextField jtxt,
int xpos, int ypos, int tfWidth, float fsize) {
// Set the font size to 12 points
// NOTE: Have to do this before we add the text
jtxt.setFont(jtxt.getFont().deriveFont(fsize));
// Set the preferred size of the label
jtxt.setSize(tfWidth, (int) fsize + 8);
// Set the text content of the label (empty by default)
jtxt.setText("");
// Make the text field visible
jtxt.setVisible(true);
// Position the text field at coordinates (xpos, ypos)
jtxt.setLocation(xpos, ypos);
// Add the text field to the window's content pane
jf1.add(jtxt); // Assuming jf1 is the main window object
// Request the window to be redrawn, reflecting the added text field
jf1.repaint();
}
/**
* Helper method to set up a JComboBox. It optionally populates
* items from a provided String array, sets font/size, and attaches
* a listener to update the selected label.
*/
private void setupCombo(JFrame jf1, JComboBox jcmbo,
int xpos, int ypos, int cmboWidth,
float fsize, String[] comboItems) {
// Set the font size to 12 points
// NOTE: Have to do this before we add the text
jcmbo.setFont(jcmbo.getFont().deriveFont(fsize));
// Set the preferred size of the label
jcmbo.setSize(cmboWidth, (int) fsize + 8);
// Make the combo box visible
jcmbo.setVisible(true);
// Enable the combo box so items can be selected
jcmbo.setEnabled(true);
// Position the combo box at coordinates (xpos, ypos)
jcmbo.setLocation(xpos, ypos);
// If the comboItems array is not null, add them all to the combo box
if (comboItems != null) {
for (String item : comboItems) {
jcmbo.addItem(item);
}
}
// Add the combo box to the window's content pane
jf1.add(jcmbo); // Assuming jf1 is the main window object
// Request the window to be redrawn, reflecting the added combo box
jf1.repaint();
// Add an ActionListener to update the "lblSelected" label
// whenever a new item is chosen
jcmbo.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
lblSelected.setText(String.valueOf(jcmbo.getSelectedItem()));
}
});
}
/**
* Helper method to create a JButton, position it, set its text,
* attach an ActionListener and a KeyListener, and finally
* add it to the frame.
*/
private void setTheButtons(JFrame jf1, JButton bttnABttn,
int xpos, int ypos, int bttnWidth,
String bttnText, float fsize) {
// Set the font size to 12 points
// NOTE: Have to do this before we add the text
bttnABttn.setFont(bttnABttn.getFont().deriveFont(fsize));
// Set the preferred size of the label
bttnABttn.setSize(bttnWidth, (int) fsize + 8);
// Set the text content of the button
bttnABttn.setText(bttnText);
// Make the button visible
bttnABttn.setVisible(true);
// Position the button at the specified coordinates
bttnABttn.setLocation(xpos, ypos);
// This action listener listens for the mouse click
bttnABttn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
theButtonAction(bttnText);
}
});
// This key listener is for listening for the keyboard actions
bttnABttn.addKeyListener(new KeyListener() {
// For Reference
@Override
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {
// No action needed here
}
// listen only for the "Enter" key
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
if (e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER) {
theButtonAction(bttnText);
}
}
// For Reference
@Override
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
// No action needed here
}
});
// Add the button to the window's content pane
jf1.add(bttnABttn); // Assuming jf1 is the main window object
// Request the window to be redrawn, reflecting the added button
jf1.repaint();
}
/**
* theButtonAction method decides what action to perform based on
* the text label of the clicked button.
*
* @param bttnText the button's text, used to identify the intended action
*/
private void theButtonAction(String bttnText) {
switch (bttnText) {
case "Add Item" -> {
String xAddItem = "";
xAddItem = txtField.getText();
//check to see if the box is not empty
// NOTE: if you want to add it then alphabetize it,
// remove all of the items to an arraylist, sort the arraylist,
// remove all of the comboBox items, and then readd them
// back from the arraylist
if (xAddItem.length() > 0) {
comboBox.addItem(txtField.getText());
txtField.setText(null);
}
}
case "Remove Selected" -> {
// Removes the currently selected item from the combo box
comboBox.removeItemAt(comboBox.getSelectedIndex());
comboBox.repaint();
}
case "Remove Last" -> {
// Removes the last item in the combo box
comboBox.removeItemAt(comboBox.getItemCount()-1);
comboBox.repaint();
}
}
}
// Remove Last
} // End Of Class ------------------------------------------------
/**
* J2x_20_comboBoxes is the main class containing the entry point of the program.
*/
public class J2x_20_comboBoxes {
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
* The main method creates an instance of ComboBoxDemo, which sets up the GUI.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ComboBoxDemo myComboDemo = new ComboBoxDemo();
}
}
Updated: 2/20/2025